Individualized mRNA vaccines evoke durable T cell immunity in adjuvant TNBC
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is frequently associated with metastatic relapse, even at an early stage.
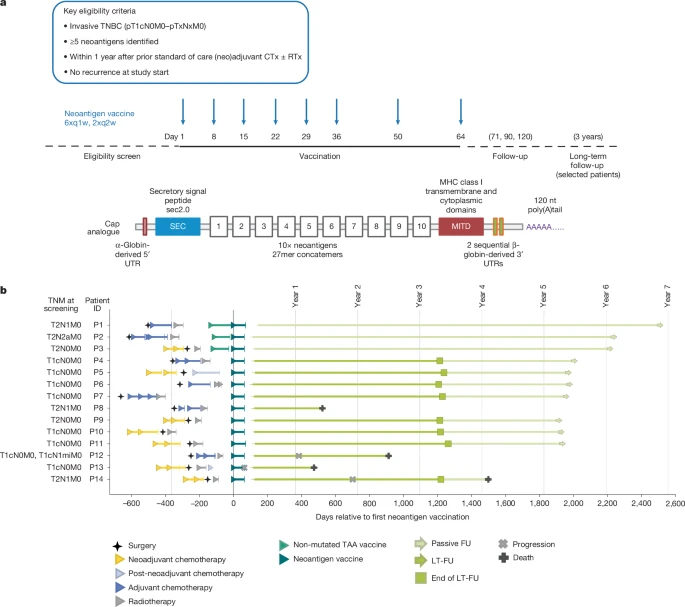
Here we assessed an individualized neoantigen mRNA vaccine in 14 patients with TNBC following surgery and after neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy. In peripheral blood of nearly all patients, high-magnitude, vaccine-induced, mostly de novo T cell responses to multiple neoantigens were detected that remained functional for several years. Characterization of individual patients revealed that a large proportion of these T cells developed into two subsets: a late-differentiated phenotype with markers indicative of ‘ready-to-act’ cytotoxic effector T cells, and T cells with a stem cell-like memory phenotype. Eleven patients remained relapse-free for up to six years post-vaccination.
Recurrence occurred in three patients: the individual with the weakest vaccine-induced T cell response relapsed, but achieved complete remission on subsequent anti-PD-1 therapy; another patient had a tumour with low major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression with MHC class I-deficient cells growing out under vaccination; and the third patient was BRCA-positive and had a recurrence from a genetically distinct primary tumour. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of individualized RNA vaccines in TNBC, document persistence of vaccine-induced, functional neoantigen-specific T cells and provide insights into possible immune escape mechanisms that will guide future approaches.
Reference: U. Sahin et al, Nature 2026
GWAS of major anxiety disorders in 122,341 European-ancestry cases
The major anxiety disorders (ANX; including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder and phobias) are highly prevalent, often onset early and cause substantial global disability.
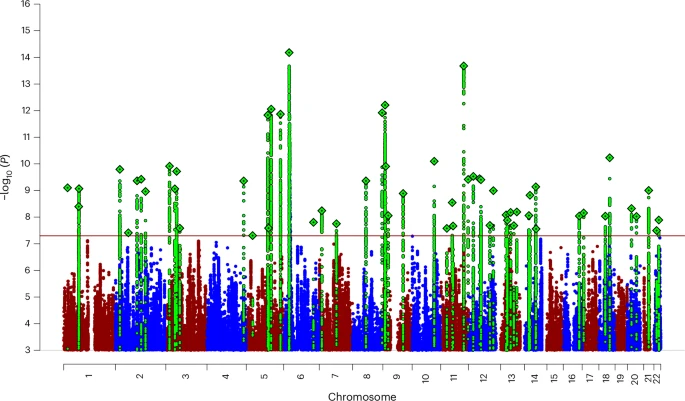
Although distinct in their clinical presentations, they probably represent differential expressions of a dysregulated threat–response system. Here, we present a genome-wide association meta-analysis comprising 122,341 European ancestry ANX cases and 729,881 controls. We identified 58 independent genome-wide significant risk variants and 66 genes with robust biological support. In an independent sample of 1,175,012 self-report ANX cases and 1,956,379 controls, 51 out of the 58 associations replicated.
As predicted by twin studies, we found substantial genetic correlation between ANX and depression, neuroticism and other internalizing phenotypes. Follow-up analyses demonstrated enrichment in all major brain regions and highlighted GABAergic signaling as one potential mechanism implicated in ANX genetic risk. These results advance our understanding of the genetic architecture of ANX and prioritize genes for functional follow-up studies.
Reference: Nora I. Strom et al, Nature genetics , 2026
Integrative epigenetics and transcriptomics identify aging genes in human blood
Recent epigenome-wide studies have identified a large number of genomic regions that consistently exhibit changes in their methylation status with aging across diverse populations, but the functional consequences of these changes are largely unknown.
On the other hand, transcriptomic changes are more easily interpreted than epigenetic alterations, but previously identified age-related gene expression changes have shown limited replicability across populations. Here, we develop an approach that leverages high-resolution multi-omic data for an integrative analysis of epigenetic and transcriptomic age-related changes and identify genomic regions associated with both epigenetic and transcriptomic age-dependent changes in blood.
Our results show that these multi-omic aging genes in blood are enriched for adaptive immune functions, replicate more robustly across diverse populations and are more strongly associated with aging-related outcomes compared to the genes identified using epigenetic or transcriptomic data alone. These multi-omic aging genes may serve as targets for epigenetic editing to facilitate cellular rejuvenation.
Reference: Mahdi Moqri et al Nature communications, 2026
zAvatar-test- A functional precision model to personalize ovarian cancer treatments: Results from a co-clinical study
In ovarian cancer, 80% of patients relapse after first-line therapy. In recurrent cases, oncologists lack reliable tests to guide chemotherapy choices, creating an unmet clinical need.

Here, we develop the ovarian cancer zebrafish Avatar-test, a functional in vivo model using patient tumor cells implanted in zebrafish embryos to predict treatment responses. We present the largest observational study (32 patients), where the zAvatar-test achieves 91% accuracy in predicting patient outcomes. Patients with a zAvatar-sensitive-test correlate with longer progression-free survival (17 vs. 6 months).
Tumors in zAvatars are dynamic, with human-host cell interactions, and higher metastatic potential in poor-prognosis cases. Finally, as a proof of concept, we demonstrate that venetoclax has the potential to sensitize multidrug-resistant tumors. Altogether, this clinical study demonstrates that the zAvatar-test may help clinicians personalize treatments for ovarian cancer patients. We are now conducting a multicentric randomized clinical trial to evaluate the zAvatar-test as a companion tool in clinical oncology.
Reference: Marta F. Estrada et al, Cell Reports Medicine, 2025
Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of aortic stenosis enhance therapeutic target discovery and disease prediction
Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common valvular heart disease and has no pharmacological therapies.
We performed a multi-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of 86,864 AS cases among 2,853,408 individuals, discovering 241 autosomal independent risk loci and 3 X chromosome risk loci. We additionally performed sex-stratified and ancestry-stratified genome-wide association studies (GWASs), identifying an additional 5 sex-specific risk loci, 11 risk loci in European ancestry individuals and 1 risk locus in African ancestry individuals. We also performed a transcriptome-wide association study using expression quantitative trait loci from human aortic valves, discovering 54 new genes for which genetically predicted expression influences the risk of AS.
We then generated a new polygenic risk score for AS. Finally, we performed gene silencing experiments targeting biologically relevant genes identified by our GWAS. Silencing of CMKLR1 and LTBP4 in human valvular interstitial cells substantially decreased mineralization, implicating a role for polyunsaturated fatty acids and transforming growth factor β signaling in AS.
Reference: Aeron M. Small et al, Nature Genetics, 2025
An integrated view of the structure and function of the human 4D nucleome
The dynamic three-dimensional (3D) organization of the human genome (the 4D nucleome) is linked to genome function.
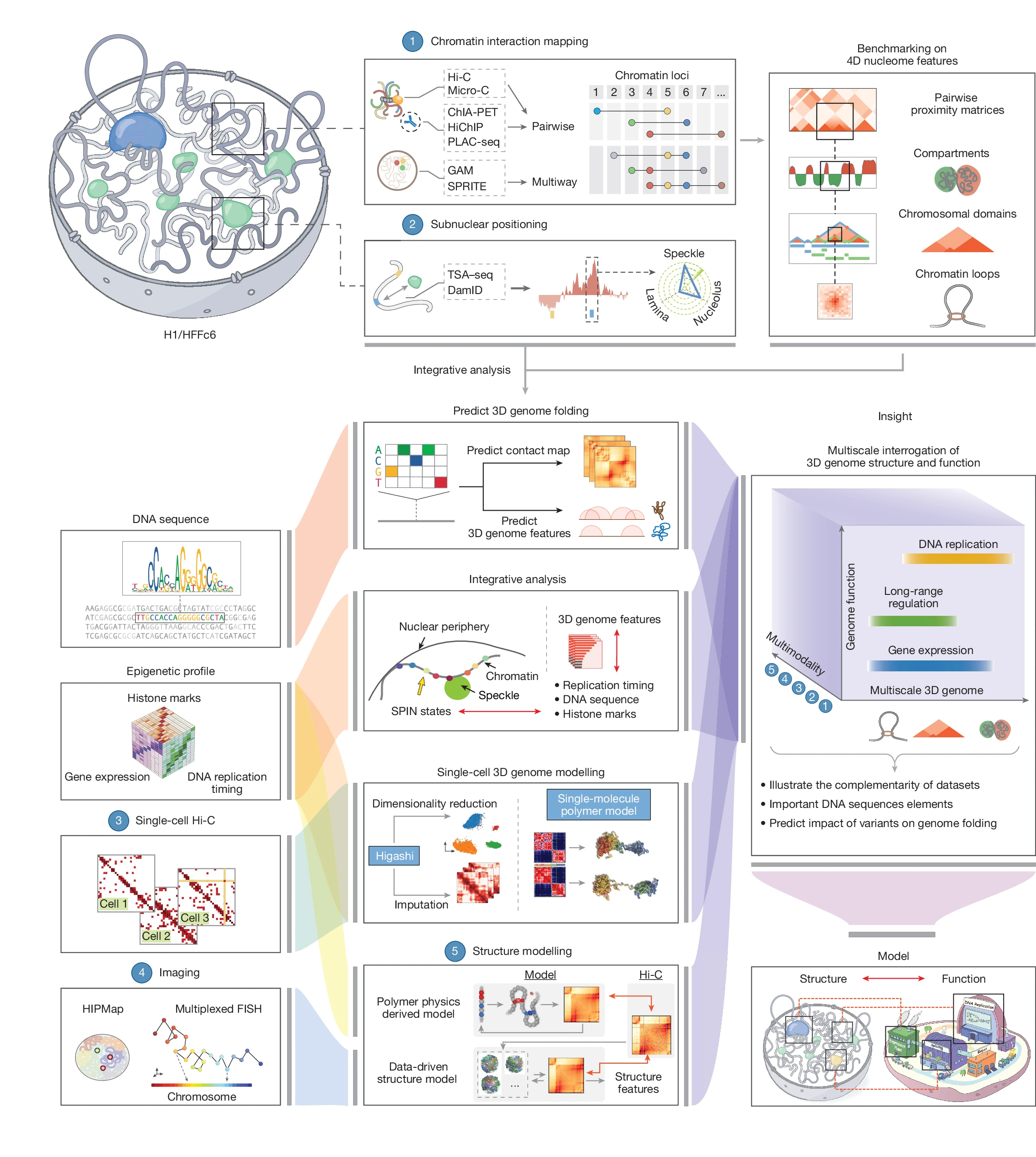
Here we describe efforts by the 4D Nucleome Project1 to map and analyse the 4D nucleome in widely used H1 human embryonic stem cells and immortalized fibroblasts (HFFc6). We produced and integrated diverse genomic datasets of the 4D nucleome, each contributing unique observations, which enabled us to assemble extensive catalogues of more than 140,000 looping interactions per cell type, to generate detailed classifications and annotations of chromosomal domain types and their subnuclear positions, and to obtain single-cell 3D models of the nuclear environment of all genes including their long-range interactions with distal elements.
Through extensive benchmarking, we describe the unique strengths of different genomic assays for studying the 4D nucleome, providing guidelines for future studies. Three-dimensional models of population-based and individual cell-to-cell variation in genome structure showed connections between chromosome folding, nuclear organization, chromatin looping, gene transcription and DNA replication. Finally, we demonstrate the use of computational methods to predict genome folding from DNA sequence, which will facilitate the discovery of potential effects of genetic variants, including variants associated with disease, on genome structure and function.
Reference: Job Dekker et al, Nature , 2025.
An open-source screening platform accelerates discovery of drug combinations
Drug combinations are essential to modern medicine, but their discovery remains slow and inefficient as experimental complexity expands rapidly with each additional drug tested. Although modern liquid handling systems enable complex and highly customizable experimental designs, a lack of strategies integrating these technologies with combination-specific analytical methods has limited throughput.
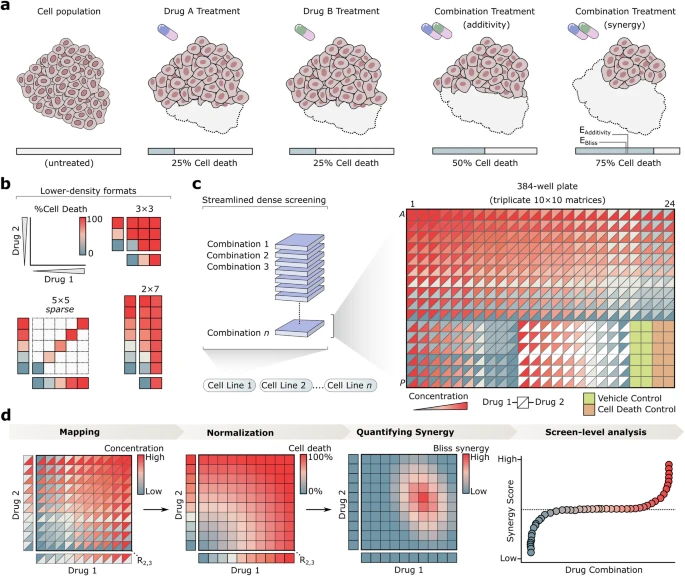
Here we introduce Combocat, an open-source and streamlined framework that combines acoustic liquid handling protocols with machine learning-based inference to achieve ultrahigh-throughput drug combination screening. Using Combocat, we generate a reference dataset of over 800 unique combinations in a dense 10 × 10 matrix format across multiple cell types, and use this to train a predictive model that accurately infers drug combination effects from sparse data, drastically reducing the number of experimental measurements required.
As proof of concept, we screened 9,045 combinations in a neuroblastoma cell line—the largest number of combinations tested in a single cell line to date—achieved using minimal resources. By integrating advanced drug dispensing technologies with predictive computational modeling, Combocat provides a scalable solution to accelerate the discovery of novel drug combinations.
Reference: William C. Wright et al, Nature Communications, 2025
Multimodal AI generates virtual population for tumor microenvironment modeling
The tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) critically impacts cancer progression and immunotherapy response. Multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF) is a powerful imaging modality for deciphering TIME, but its applicability is limited by high cost and low throughput.

We propose GigaTIME, a multimodal AI framework for population-scale TIME modeling by bridging cell morphology and states. GigaTIME learns a cross-modal translator to generate virtual mIF images from hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slides by training on 40 million cells with paired H&E and mIF data across 21 proteins.
We applied GigaTIME to 14,256 patients from 51 hospitals and over 1,000 clinics across seven US states in Providence Health, generating 299,376 virtual mIF slides spanning 24 cancer types and 306 subtypes. This virtual population uncovered 1,234 statistically significant associations linking proteins, biomarkers, staging, and survival. Such analyses were previously infeasible due to the scarcity of mIF data. Independent validation on 10,200 TCGA patients further corroborated our findings.
Reference: Jeya Maria Jose Valanarasu et al, Cell, 2025
Whole-genome landscapes of 1,364 breast cancers
Breast cancer remains a major global health challenge. Here, to comprehensively characterize its genomic landscape and the clinical significance of genomic characteristics, we analysed whole-genome sequences from 1,364 clinically annotated breast cancers, with transcriptome data available for most cases.
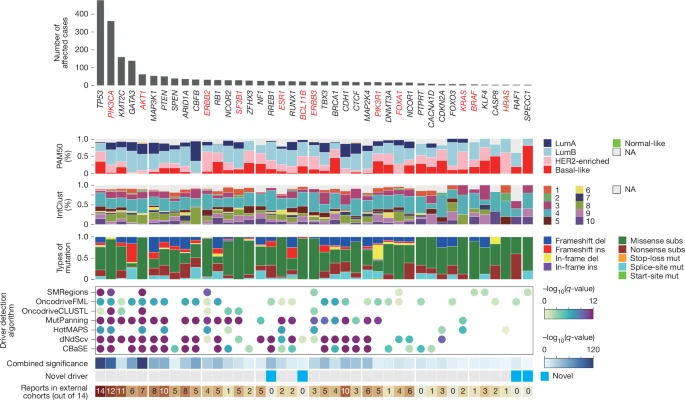
Our study expands the repertoire of oncogenic alterations and identifies novel driver genes, recurrent gene fusions, structural variants and copy number alterations. Timing analyses on copy number alterations suggest that genomic instability emerges decades before tumour diagnosis, and offer insights into early initiation of tumorigenesis.
Pattern-driven genomic features, including mutational signatures, homologous recombination deficiency, tumour mutational burden and tumour heterogeneity scores, were associated with clinical outcomes, highlighting their potential utility as predictive biomarkers for clinical evaluation of treatments such as CDK4/6 and HER2 inhibitors, as well as adjuvant and neoadjuvant chemotherapy. These findings highlight the power of large-scale, clinically annotated whole-genome sequencing in advancing our understanding of how genomic alterations shape patient outcomes.
Reference Ryul Kim, Jonghan Yu et al, Nature 2025.
A genome-wide association study of mass spectrometry proteomics using a nanoparticle enrichment platform
Most studies to date of protein quantitative trait loci (pQTLs) have relied on affinity proteomics platforms, which provide only limited information about the targeted protein isoforms and may be affected by genetic variation in their epitope binding.
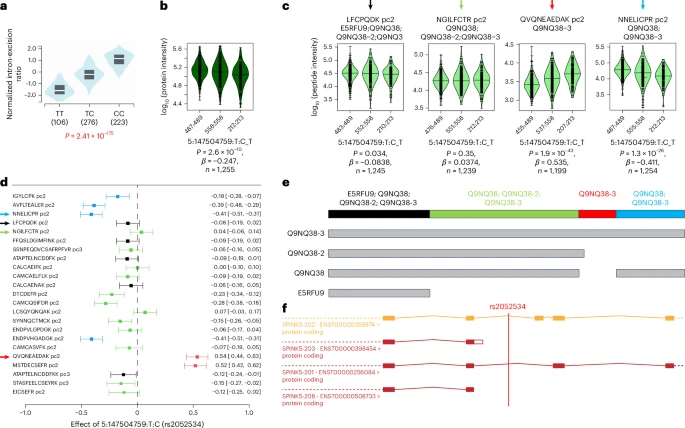
Here we show that mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics can complement these studies and provide insights into the role of specific protein isoform and epitope-altering variants. Using the Seer Proteograph nanoparticle enrichment MS platform, we identified and replicated new pQTLs in a genome-wide association study of proteins in blood plasma samples from two cohorts and evaluated previously reported pQTLs from affinity proteomics platforms.
We found that >30% of the evaluated pQTLs were confirmed by MS proteomics to be consistent with the hypothesis that genetic variants induce changes in protein abundance, whereas another 30% could not be replicated and are possibly due to epitope effects, although alternative explanations for nonreplication need to be considered on a case-by-case basis. Reference: Karsten Suhre et al, Nature Genetics 2025
Microbial signals in primary and metastatic brain tumors
Gliomas and brain metastases are associated with poor prognosis, necessitating a deeper understanding of brain tumor biology and the development of effective therapeutic strategies. Although our group and others have demonstrated microbial presence in various tumors, recent controversies regarding cancer-type-specific intratumoral microbiota emphasize the importance of rigorous, orthogonal validation.
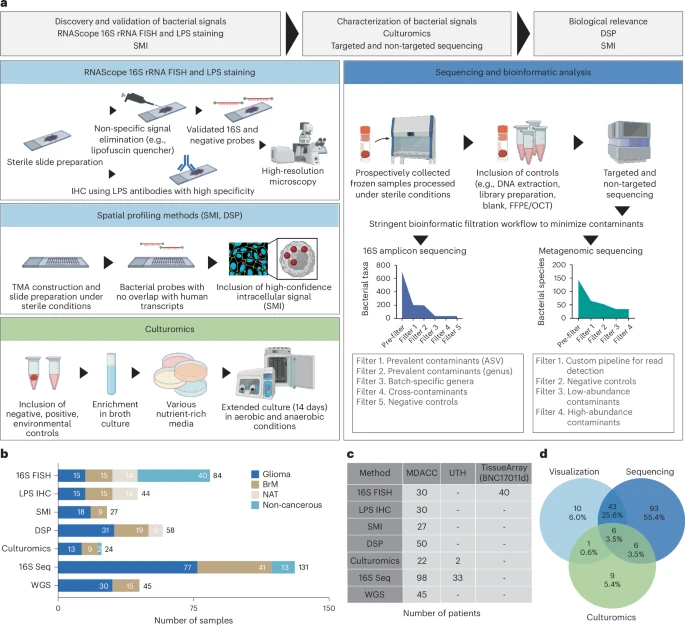
This prospective, multi-institutional study included a total of 243 samples from 221 patients, comprising 168 glioma and brain metastases samples and 75 non-cancerous or tumor-adjacent tissues. Using stringent fluorescence in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry and high-resolution spatial imaging, we detected intracellular bacterial 16S rRNA and lipopolysaccharides in both glioma and brain metastases samples, localized to tumor, immune and stromal cells.
Custom 16S and metagenomic sequencing workflows identified taxa associated with intratumoral bacterial signals in the tumor microenvironment; however, standard culture methods did not yield readily cultivable microbiota. Spatial analyses revealed significant correlations between bacterial 16S signals and antimicrobial and immunometabolic signatures at regional, neighborhood and cellular levels. Furthermore, intratumoral 16S bacterial signals showed sequence overlap with matched oral and gut microbiota, suggesting a possible connection with distant communities. Together, these findings introduce microbial elements as a component of the brain tumor microenvironment and lay the foundation for future mechanistic and translational studies. Reference: Golnaz Morad et al, Nature Medicine, 2025
GWAS identify distinct genetic architectures for early-onset and late-onset depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a common and heterogeneous disorder of complex etiology. Studying more homogeneous groups stratified according to clinical characteristics, such as age of onset, can improve the identification of the underlying genetic causes and lead to more targeted treatment strategies.
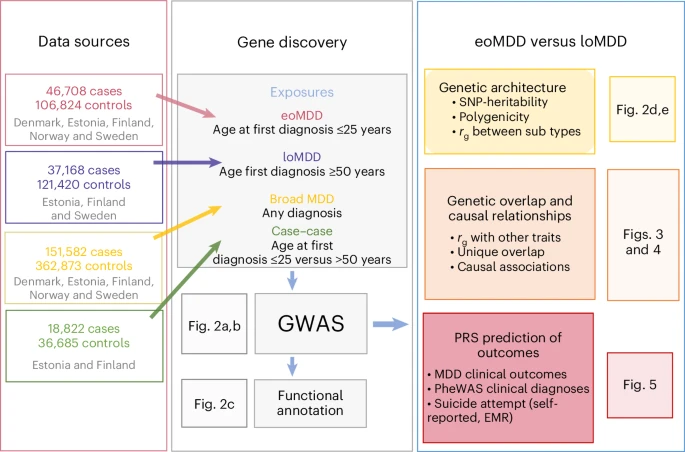
We leveraged Nordic biobanks with longitudinal health registries to investigate differences in the genetic architectures of early-onset (eoMDD; n = 46,708 cases) and late-onset (loMDD; n = 37,168 cases) MDD. We identified 12 genomic loci for eoMDD and two for loMDD. Overall, the two MDD subtypes correlated moderately (genetic correlation, rg = 0.58) and differed in their genetic correlations with related traits.
These findings suggest that eoMDD and loMDD have partially distinct genetic signatures, with a specific developmental brain signature for eoMDD. Importantly, we demonstrate that polygenic risk scores (PRS) for eoMDD predict suicide attempts within the first 10 years after the initial diagnosis: the absolute risk for suicide attempt was 26% in the top PRS decile, compared to 12% and 20% in the bottom decile and the intermediate group, respectively. Taken together, our findings can inform precision psychiatry approaches for MDD. Reference: John R. Shorter et al, Nature Genetics (2025)
A human pan-disease blood atlas of the circulating proteome
The human blood proteome provides a holistic readout of health states through the assessment of thousands of circulating proteins.

Here, we present a pan-disease resource to enable the study of diverse disease phenotypes within a harmonized proteomics dataset. By profiling protein concentrations across 59 diseases and healthy cohorts, we identified proteins associated with age, sex, and BMI, as well as disease-specific signatures. This study highlights shared and distinct protein patterns across conditions, demonstrating the power of a unified proteomics approach to uncover biological insights. The dataset, covering 8,262 individuals and up to 5,416 proteins, serves as an online resource for exploring disease-specific protein profiles and advancing precision medicine research.
Reference : Maria Bueno Alvez et al, Science 2025
Basal cell of origin resolves neuroendocrine–tuft lineage plasticity in cancer
Neuroendocrine and tuft cells are rare chemosensory epithelial lineages defined by the expression of ASCL1 and POU2F3 transcription factors, respectively. Neuroendocrine cancers, including small cell lung cancer (SCLC), frequently display tuft-like subsets, a feature linked to poor patient outcomes.
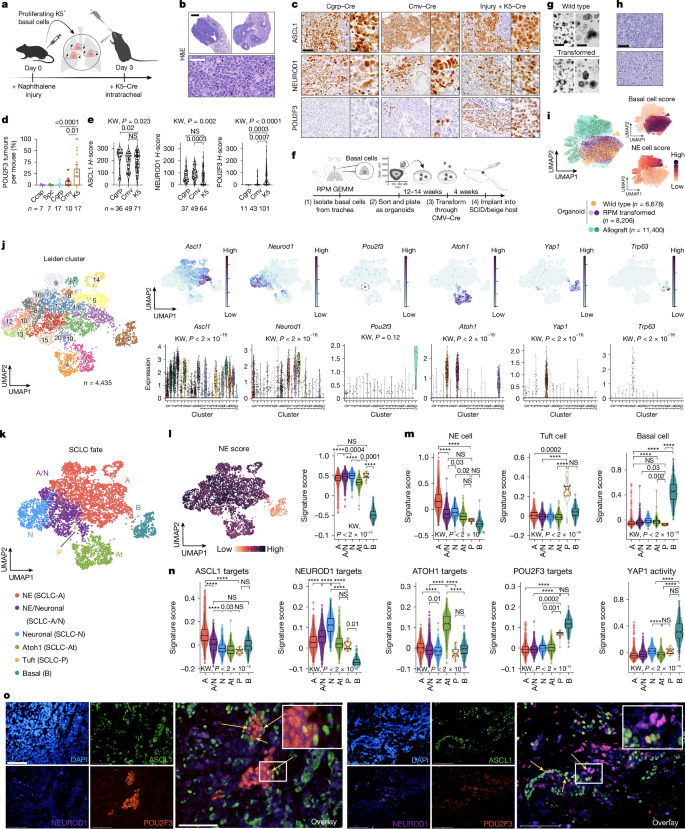
The mechanisms driving neuroendocrine–tuft tumour heterogeneity and the origins of tuft-like cancers are unknown. Using multiple genetically engineered animal models of SCLC, we demonstrate that a basal cell of origin (but not the accepted neuroendocrine origin) generates neuroendocrine–tuft-like tumours that highly recapitulate human SCLC. Single-cell clonal analyses of basal-derived SCLC further uncovered unexpected transcriptional states, including an Atoh1+ state, and lineage trajectories underlying neuroendocrine–tuft plasticity.
Transcriptomics of 944 human SCLCs revealed a basal-like subset and a tuft–ionocyte-like state that altogether demonstrate notable conservation between cancer states and normal basal cell injury response mechanisms. Together, these data indicate that the basal cell is a probable origin for SCLC and other neuroendocrine–tuft cancers that can explain neuroendocrine–tuft heterogeneity, offering new insights for targeting lineage plasticity.
Reference: Abbie S. Ireland et al, Nature 2025
Mapping the Bonobo Gut: A Groundbreaking Atlas of Gut Bacteria and Their Influences
In great apes, the gut bacteriome shapes key physiological functions and is influenced by both the exposome and the host. Yet, isolating these independent contributions remains challenging.

We sequenced 644 fecal samples from 212 wild and zoo-housed bonobos (Pan paniscus), matched with detailed data collection on host and exposome factors. This standardized dataset reveals clear differences in gut bacterial diversity and composition between wild and captive bonobos.
Within the controlled zoo-housed cohort, factors such as age, transit time, diet, early life adversity, and medication use influence gut bacterial structure. Notably, social contact emerges as a stronger predictor of bacteriome similarity than genetics or other exposome factors, while maternal effects persist even in non-cohabiting mother-offspring dyads. By offering a unique, comprehensive, and standardized dataset, our work paves the way for future research into microbiome ecology, providing insights with far-reaching implications for both human and animal health in an increasingly industrialized world.
Reference: Jonas R.R. Torfs 0000-0001-7102-6265 et al Cell Reports, 2025
Noncoding rare variant associations with blood traits in 166,740 UK Biobank genomes
Large biobanks with whole-genome sequencing (WGS) now enable the association of noncoding rare variants with complex human traits. Given that >98% of the genome is available for exploration, the selection of noncoding variants remains a critical yet unresolved challenge in these analyses.
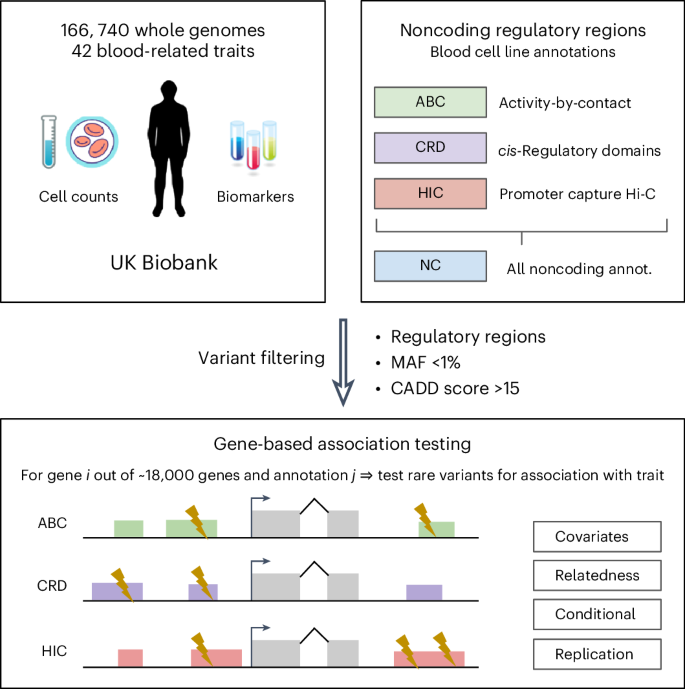
Here we leverage knowledge of blood gene regulation and deleteriousness scores to select noncoding variants pertinent for association with blood-related traits. Integrating WGS and 42 blood cell count and biomarker measurements for 166,740 UK Biobank samples, we perform variant collapsing tests, identifying hundreds of gene–trait associations involving noncoding variants.
However, we demonstrate that most of these noncoding rare variant associations (1) reproduce associations known from previous studies and (2) are driven by linkage disequilibrium between nearby common and rare variants. This study underscores the prevailing challenges in rare variant analysis and the need for caution when interpreting noncoding rare variant association results.
Reference: Diogo M. Ribeiro et al, Nature Genetics, 2025
scplainer: using linear models to understand MS-based single-cell proteomics data
Analyzing mass spectrometry (MS)-based single-cell proteomics (SCP) data faces important challenges inherent to MS-based technologies and single-cell experiments.
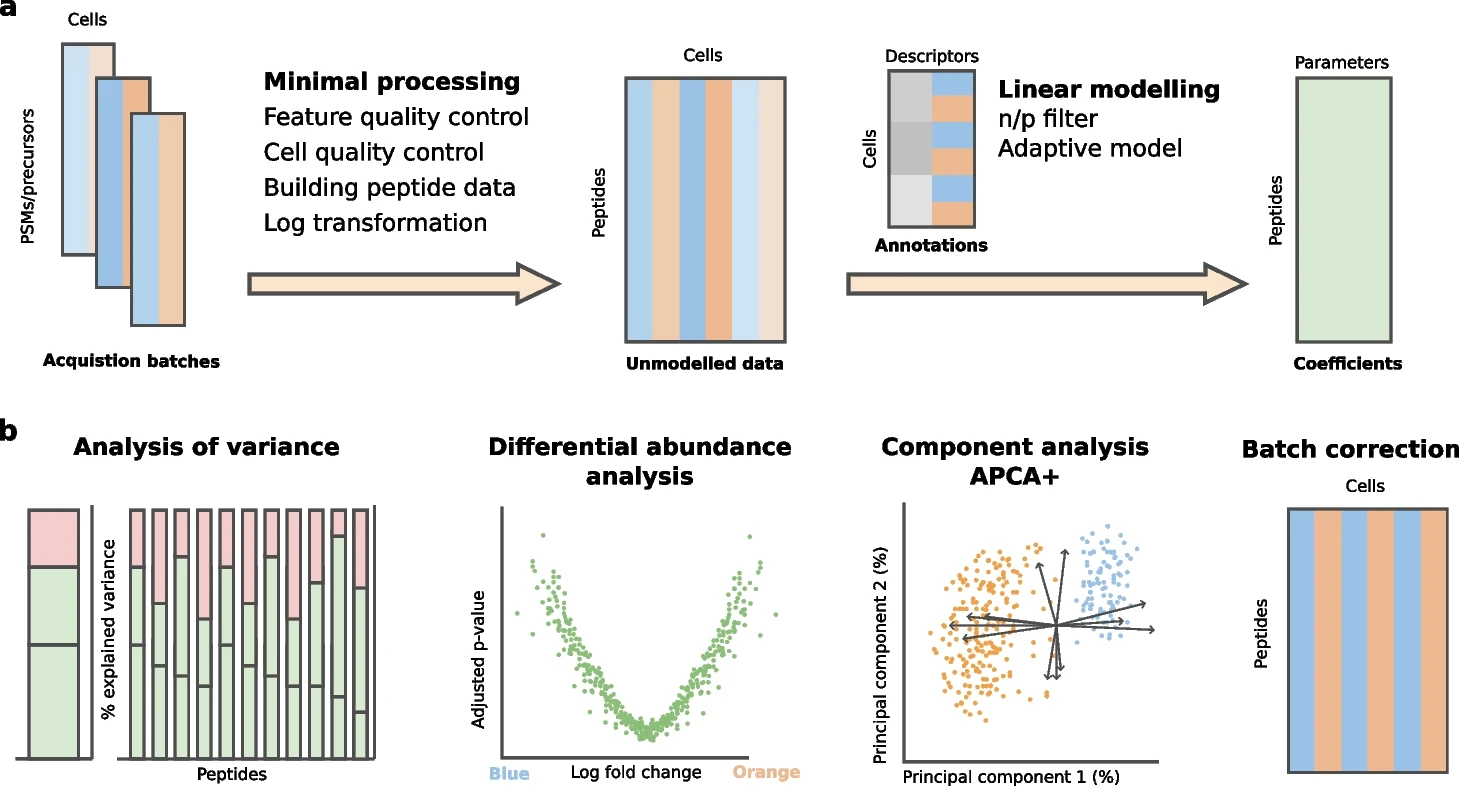
We present scplainer, a principled and standardized approach for extracting meaningful insights from SCP data using minimal data processing and linear modeling. scplainer performs variance analysis, differential abundance analysis, and component analysis while streamlining result visualization. scplainer effectively corrects for technical variability, enabling the integration of data sets from different SCP experiments. In conclusion, this work reshapes the analysis of SCP data by moving efforts from dealing with the technical aspects of data analysis to focusing on answering biologically relevant questions. Reference : Christophe Vanderaa et al, Genome Biology volume 26, Article number: 237 (2025)
Deep phenotyping of health–disease continuum in the Human Phenotype Project
The Human Phenotype Project (HPP) is a large-scale deep-phenotype prospective cohort. To date, approximately 28,000 participants have enrolled, with more than 13,000 completing their initial visit.
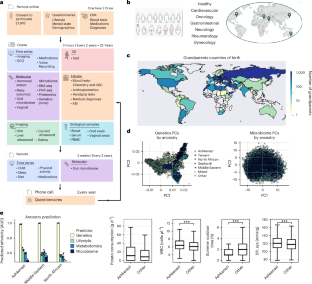
The project is aimed at identifying novel molecular signatures with diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic value, and at developing artificial intelligence (AI)-based predictive models for disease onset and progression. The HPP includes longitudinal profiling encompassing medical history, lifestyle and nutrition, anthropometrics, blood tests, continuous glucose and sleep monitoring, imaging and multi-omics data, including genetics, transcriptomics, microbiome (gut, vaginal and oral), metabolomics and immune profiling.
Analysis of these data highlights the variation of phenotypes with age and ethnicity and unravels molecular signatures of disease by comparison with matched healthy controls. Leveraging extensive dietary and lifestyle data, we identify associations between lifestyle factors and health outcomes. Finally, we present a multi-modal foundation AI model, trained using self-supervised learning on diet and continuous-glucose-monitoring data, that outperforms existing methods in predicting disease onset. This framework can be extended to integrate other modalities and act as a personalized digital twin. In summary, we present a deeply phenotyped cohort that serves as a platform for advancing biomarker discovery, enabling the development of multi-modal AI models and personalized medicine approaches.
Reference: Nature Medicine, Lee Reicher et al (2025)
A map of blood regulatory variation in South Africans enables GWAS interpretation
Functional genomics resources are critical for interpreting human genetic studies, but currently they are predominantly from European-ancestry individuals.
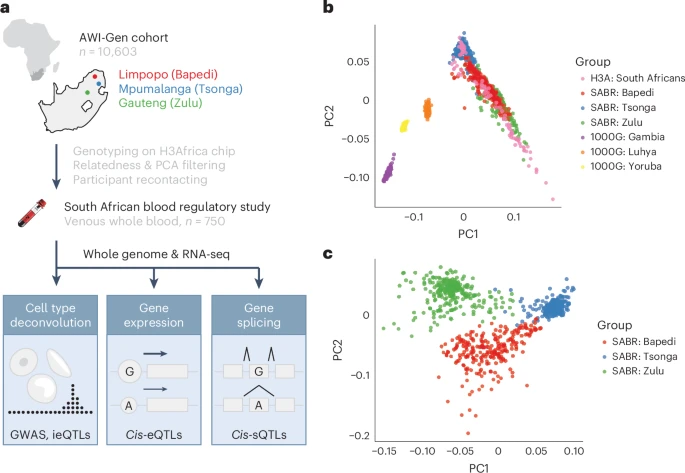
Here we present the South African Blood Regulatory (SABR) resource, a map of blood regulatory variation that includes three South Eastern Bantu-speaking groups. Using paired whole-genome and blood transcriptome data from over 600 individuals, we map the genetic architecture of 40 blood cell traits derived from deconvolution analysis, as well as expression, splice and cell-type interaction quantitative trait loci.
We comprehensively compare SABR to the Genotype Tissue Expression Project and characterize thousands of regulatory variants only observed in African-ancestry individuals. Finally, we demonstrate the increased utility of SABR for interpreting African-ancestry association studies by identifying putatively causal genes and molecular mechanisms through colocalization analysis of blood-relevant traits from the Pan-UK Biobank. Importantly, we make full SABR summary statistics publicly available to support the African genomics community.
Reference: Stephane E. Castel et al Nature Genetics (2025)
The molecular impact of cigarette smoking resembles aging across tissues
Tobacco smoke is the main cause of preventable mortality worldwide. Smoking increases the risk of developing many diseases and has been proposed as an aging accelerator. Yet, the molecular mechanisms driving smoking-related health decline and aging acceleration in most tissues remain unexplored.
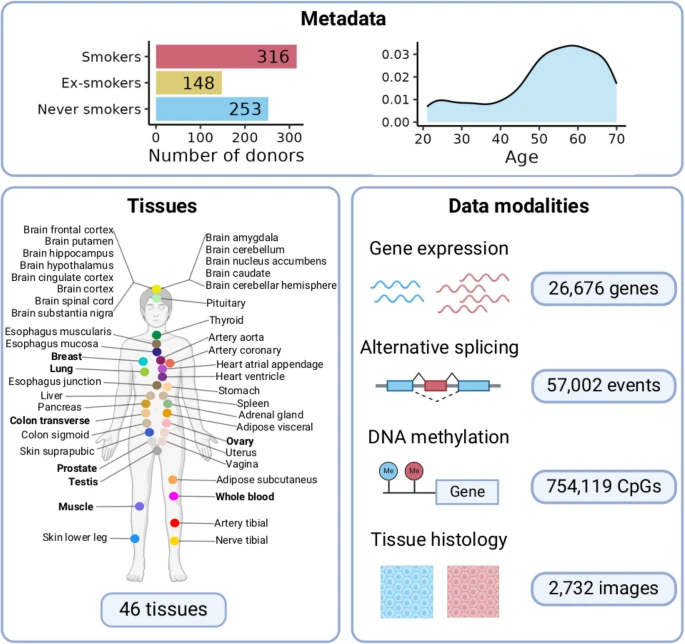
Here, we use data from the Genotype-Tissue Expression Project (GTEx) to perform a characterization of the effect of cigarette smoking across human tissues. We perform a multi-tissue analysis across 46 human tissues. Our multi-omics characterization includes analysis of gene expression, alternative splicing, DNA methylation, and histological alterations. We further analyze ex-smoker samples to assess the reversibility of these molecular alterations upon smoking cessation.
We show that smoking impacts tissue architecture and triggers systemic inflammation. We find that in many tissues, the effects of smoking significantly overlap those of aging. Specifically, both age and smoking upregulate inflammatory genes and drive hypomethylation at enhancers (odds ratio (OR) = 2). In addition, we observe widespread smoking-driven hypermethylation at target regions of the Polycomb repressive complex (OR = 2), which is a well-known aging effect. Smoking-induced epigenetic changes overlap causal aging CpGs, suggesting that these methylation changes may directly mediate the aging acceleration observed in smokers. Finally, we find that smoking effects that are shared with aging are more persistent over time. Reference: Jose Miguel Ramirez et al, Genome Medicine, 2025
A microRNA-based dynamic risk score for type 1 diabetes
Identifying individuals at high risk of type 1 diabetes (T1D) is crucial as disease-delaying medications are available.
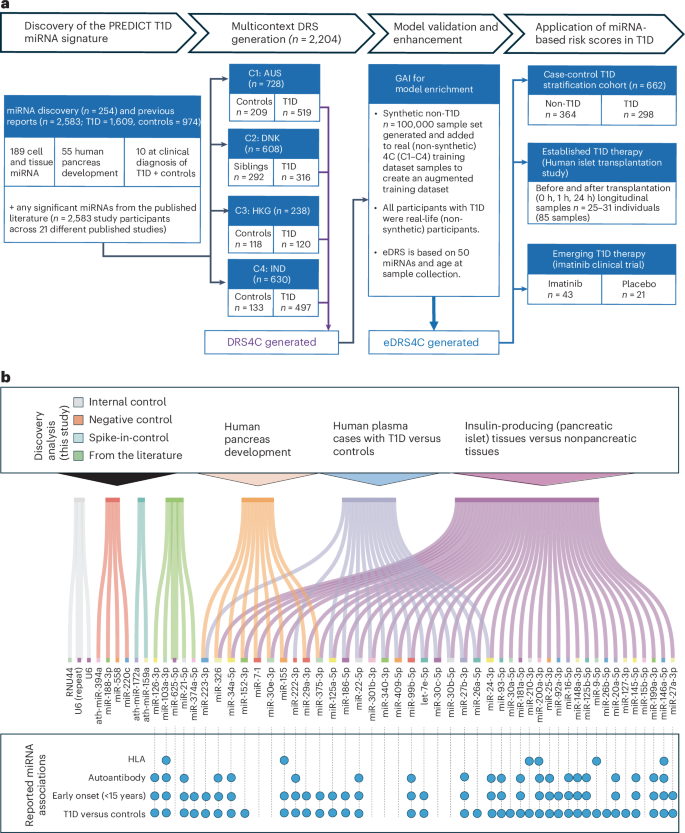
Here we report a microRNA (miRNA)-based dynamic (responsive to the environment) risk score developed using multicenter, multiethnic and multicountry (‘multicontext’) cohorts for T1D risk stratification. Discovery (wet and dry lab) analysis identified 50 miRNAs associated with functional β cell loss, which is a hallmark of T1D. These miRNAs measured across n = 2,204 individuals from four contexts (4C: Australia, Denmark, Hong Kong SAR People’s Republic of China, India) led to a four-context, miRNA-based dynamic risk score (DRS) that effectively stratified individuals with and without T1D.
Generative artificial intelligence was used to create an enhanced four-context, miRNA-based DRS, which offered good predictive power (area under the curve = 0.84) for T1D stratification in a separate multicontext validation dataset (n = 662), and accurately predicted future exogenous insulin requirement at 1 hour of islet transplantation. In a clinical trial assessing the imatinib drug therapy, baseline miRNA signature, rather than clinical characteristics, distinguished drug responders from nonresponders at 1 year. This study harnessed machine learning/generative artificial intelligence approaches, identifying and validating a miRNA-based DRS for T1D discrimination and treatment efficacy prediction. Reference: Mugdha V. Joglekar et al, Nature Medicine, 2025
Global genetic diversity of human gut microbiome species is related to geographic location and host health
The human gut harbors thousands of microbial species, each exhibiting significant inter-individual genetic variability. Although many studies have associated microbial relative abundances with human-health-related phenotypes, the substantial intraspecies genetic variability of gut microbes has not yet been comprehensively considered, limiting the potential of linking such genetic traits with host conditions.

Here, we analyzed 32,152 metagenomes from 94 microbiome studies across the globe to investigate the human microbiome intraspecies genetic diversity. We reconstructed 583 species-specific phylogenies and linked them to geographic information and species’ horizontal transmissibility.
We identified 484 microbial-strain-level associations with 241 host phenotypes, encompassing human anthropometric factors, biochemical measurements, diseases, and lifestyle. We observed a higher prevalence of a Ruminococcus gnavus clade in nonagenarians correlated with distinct plasma bile acid profiles and a melanoma and prostate-cancer-associated Collinsella clade. Our large-scale intraspecies genetic analysis highlights the relevance of strain diversity as it relates to human health. Reference: Sergio Andreu-Sánchez et al, Cell, 2025